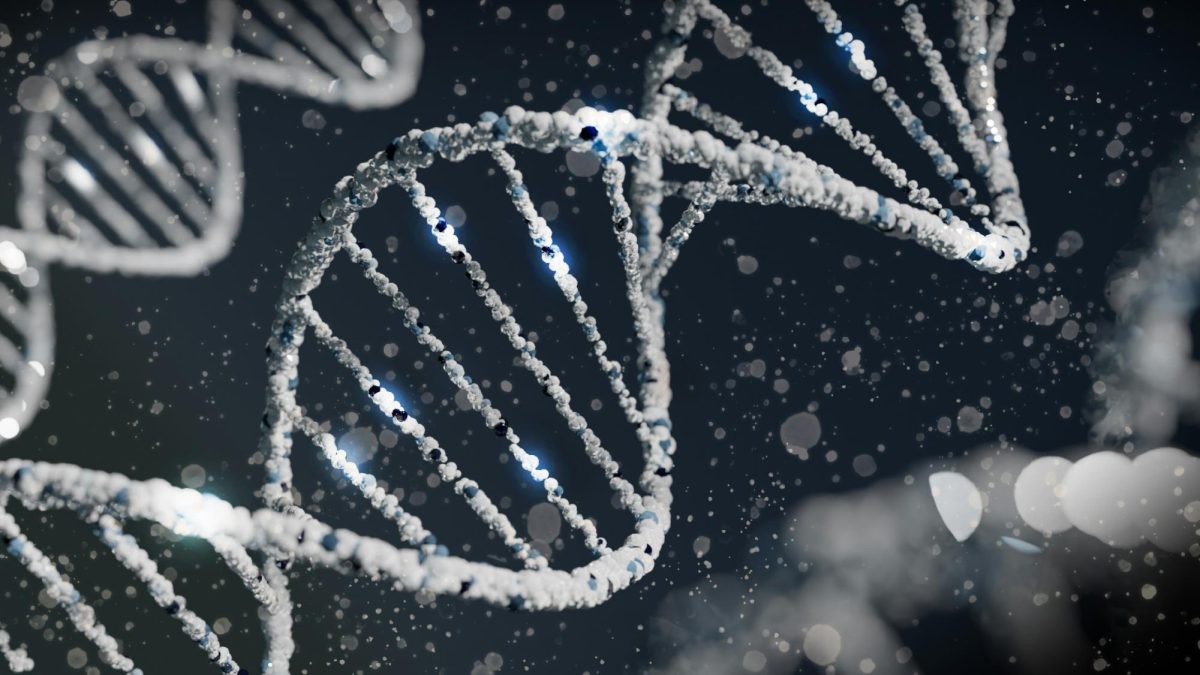
DNA is like a computer program, but far more advanced than any artificial software. Even a small defect can disrupt the working mechanism of any system. In the same way, any defect in the structure of DNA leads to health problems and diseases, not only in humans but also in animals, plants and even microbes. According to the World Health Organization, genetic diseases affect an estimate of ten out of every 1000 people, meaning that around 70 to 80 million people around the globe suffer from genetic diseases like thalassemia. With the revolutionary advancement in the field of science and technology, genes can now be modified to eliminate or prevent diseases and even treat infertility. By using these techniques, DNA can also be changed by adding or removing a specific DNA sequence to achieve certain desirable traits, causing much debate on the ethicality of such methods. Although there are many ethical concerns related to the modification of genes, its potential to protect lives surpasses the overall moral considerations.
Gene editing can be used to cure genetic diseases such as cystic fibrosis, a genetic condition that affects a protein in the body. CRISPR-Cas9, a gene editing technology where a DNA sequence is removed or replaced, is a game-changing technology in this field. Every year, about eight million children are born with genetic diseases around the globe. Health conditions like cystic fibrosis or thalassemia are hereditary diseases, thus genetic modification not only benefits the person with the health issue but their offspring as well, breaking the genetic cycle of hereditary disease.
Gene editing can also be used for the prevention or treatment of patients suffering from genetic infertility. Germline gene editing (GGE) is used to modify the embryo at its earliest stages to prevent or treat infertility. About 50% of Infertility cases are due to genetic defects. This method targets the gene to correct or modify it, to prevent it from causing various issues including infertility. GGE not only benefits the immediate affected person but also prevents the transmission of these genetic disorders to future generations.
Even though there are no clear rules and regulations regarding these procedures, changes in a gene could have negative side effects for the rest of the world. It can lead to unpredictable outcomes like allergies and possible damage to surrounding organs and tissues as research on gene editing is still in its early stages. There needs to be a set of rules that make it clear which diseases should be treated using these technologies. Another ethical issue created by this technology is the concept of designer babies, whose embryos are modified to produce a child with the parents’ desired physical traits. These treatments are currently only available to people with greater financial resources as prices currently average $2 million per patient. The National Human Genome Research Institute (NIH) states that scientists have addressed ethical concerns citing that the International Summit on Gene Editing has deemed the method safe, however, its use for reproductive difficulties and enhancements can not be justified at this time. Despite the flaws of this scientific technology, the advantages exceed the ethical concerns, improving and creating a better society.
Gene editing holds the potential to reduce inequalities in health care and improve society. With more improvements and research, the technology might also be able to treat more severe and life-threatening diseases like cancer or HIV. While this powerful technology leads to the overall growth of various fields such as healthcare and medicine, it is important to be aware of the potential consequences, be cautious about ethical considerations, and follow safety protocols that are essential to prevent misuse.